Minimum wage raised to $13.25 for small businesses, $14.25 for large businesses.
By Kai McNamee
For the third year in a row, the City of Los Angeles — along with neighboring cities such as Santa Monica — has seen an increase in minimum wage. Some small businesses on the Westside have been struggling to adjust to the increase.
As of July 1, 2019, small businesses of 25 or fewer employees must pay a minimum wage of $13.25. Large businesses of 26 or more employees must pay a minimum wage of $14.25. As outlined by the Los Angeles Minimum Wage Ordinance, the minimum wage has increased yearly since 2016; by 2020 and 2021, large and small businesses will be required to pay employees a minimum of $15 per hour, respectively. Starting July 1, 2022, the minimum wage will be adjusted annually according to the Consumer Price Index for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W), an index used to monitor cost of living published by the Bureau of Labor and Statistics.
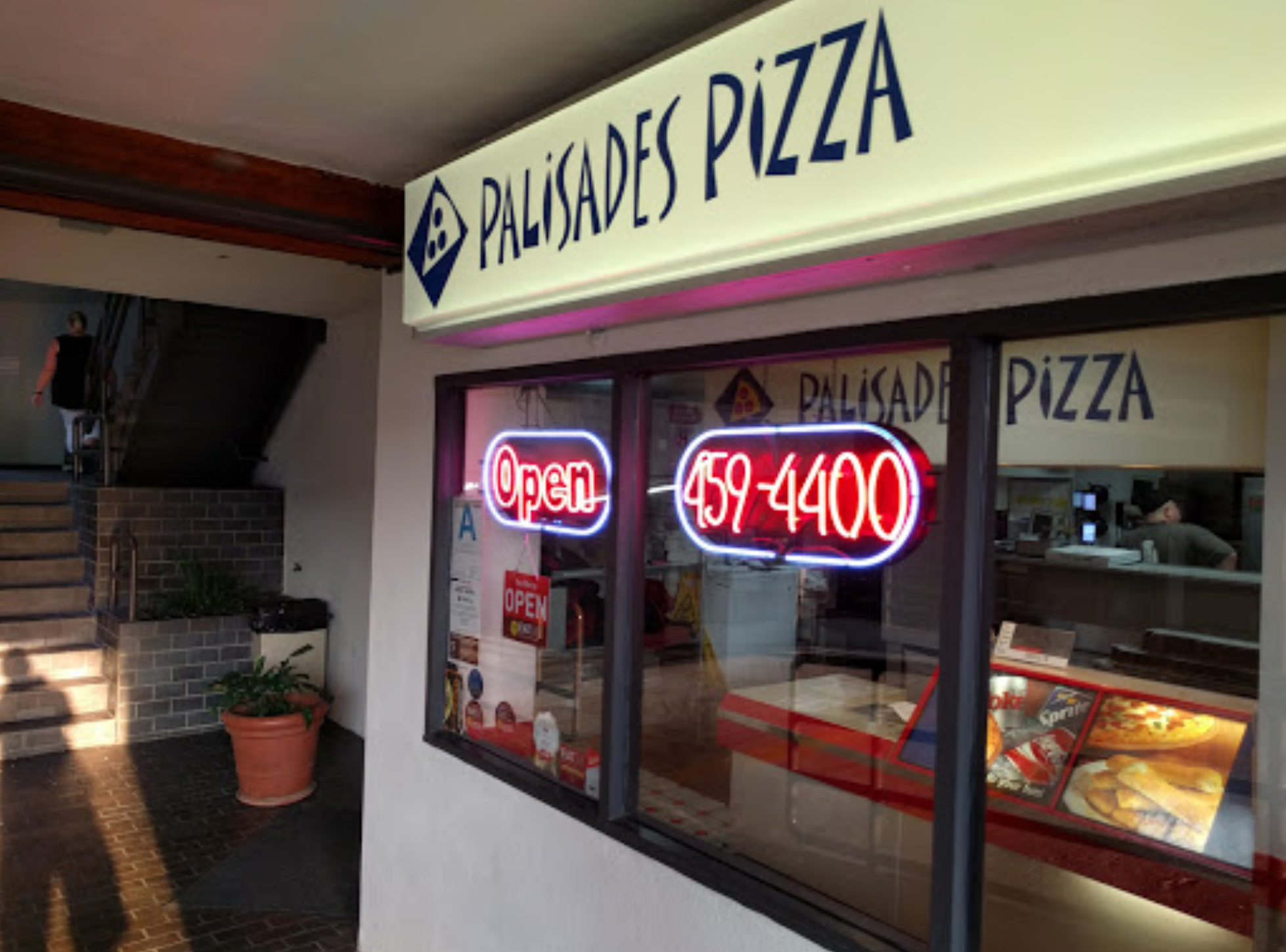
Some small businesses, like Palisades Pizza, have been forced to downsize due to the minimum wage increases. Hans Bandt, a manager and a member of the family that owns the restaurant, says the business “just can’t afford to hire more people.” To adapt, Bandt says the business has been using third party services, like DoorDash, to deliver pizza. “In a few years, we might not have any delivery guys.”
On the Westside, many are worried about the rising costs of living — some question whether or not the minimum wage will be enough to compensate for the cost of living in the area. Simone Acciai, the owner of Dolcenero Gelato on Main Street, is concerned that even a $15 minimum wage is not enough to compensate for rising costs of living. After raising the minimum wage for his employees to $13.25, Acciai says it’s “still not enough” to afford the cost of living. “I’m happy for my employees, but two to three dollars per hour more is not even close to enough.”
Across California, rising costs of living have pressured legislators to raise minimum wage. The Fight for $15, an activism campaign advocating for a federal $15 minimum wage, has been gaining momentum around the country as more cities and states begin raising minimum wage beyond the $7.25 federal level. On July 18, legislation to raise the federal minimum wage to $15 by 2025 passed in the House of Representatives, but the bill is unlikely to pass in the Senate.
For consumers, the purchasing power of a $15 minimum wage varies by region. Based on data collected by the federal Bureau of Economic Analysis in 2017, prices in the LA area are 17.1% higher than the national average. As a result, $15 has a relative purchasing power of $12.81.
To compensate for rising costs of living, the Minimum Wage Ordinance will be the first piece of legislation to index LA’s minimum wage. Similar wage ordinances adopted by Santa Monica and unincorporated parts of LA County will also use the CPI-W to adjust minimum wage on a yearly basis, starting in 2022. CPI-W is a measure of the average change in price of a fixed basket of goods and services consumed by average urban wage earners and clerical workers. According to the Bureau of Labor and Statistics, 29% of Los Angeles’s total population falls under CPI-W.
Prior to the 2016 Los Angeles Minimum Wage Ordinance, Los Angeles followed California’s minimum wage laws. BLS statistics show that CPI-W has increased roughly 43% between 2000 and 2015, calculated using 1982-1984 as the base period; Los Angeles minimum wage grew roughly 56% between 2000 and 2015. Between 2000 and 2015, the cost of living — as measured by the CPI-W — increased, and minimum wage followed similar upward trends.
But after LA adopted the Minimum Wage Ordinance in 2016, minimum wage hikes began to dramatically outpace increases in cost of living. Between 2015 and 2018, minimum wage increased by 33% and 47% for small and large businesses, respectively. In the same period, CPI-W increased by only 4%.
Numerous studies have illustrated that minimum wage hikes produce mixed results for LA wage earners and businesses alike. A 2015 Los Angeles Economic Development Corporation report reviewing four studies found “a continuum of economic impacts from the very positive to the very negative.” Increased wages can significantly benefit wage earners, but wage hikes increase expenses for businesses that rely on minimum wage labor, potentially forcing businesses to downsize and hire less workers.
Furthermore, study findings have suggested that raising the minimum wage might not be the most precise way combat poverty. The study found that of the 25% of workers in LA earning less than $13.25 per hour. The study concluded that of the 25%, these workers account for an average of 38% of total household income, and 43% of them live in households whose income is greater than the $55,000 national median. The 2015 LAEDC study found that in 2013, 30% of families living below the poverty line had no workers in their households — these families would not benefit from increased wages.