Brentwood’s iconic trees face aging and pests.
By Keldine Hull
For decades, the Brentwood community has been home to “Cultural Heritage Monument #48”- the sweeping coral trees that line San Vicente’s median. They’ve become synonymous with Brentwood and a unique part of its beauty. Nancy Freedman, Brentwood resident for over 40 years and former BCC Chair, talks about the historical significance of the coral trees as well as their importance within the community. “A Red Line train ran on the median which was removed when the politicians in mid-century decided cars would be the future and freeways the answer,” Freedman begins. “The train traveled from Santa Monica to Downtown and through a portion of the VA. In the place of tracks and train, the official tree of Los Angeles, the coral, was planted in two sections. One was Brentwood, the other continues in to Santa Monica.” Freedman continues, “It is the wrong tree for the median, but has been enjoyed for their beauty and diversity. People love the corals and feel they are the icon for our community. They are growing old and like people, we mourn their loss, but trees do die. We have attempted to give them a good life as a community contributing to them financially and emotionally.”
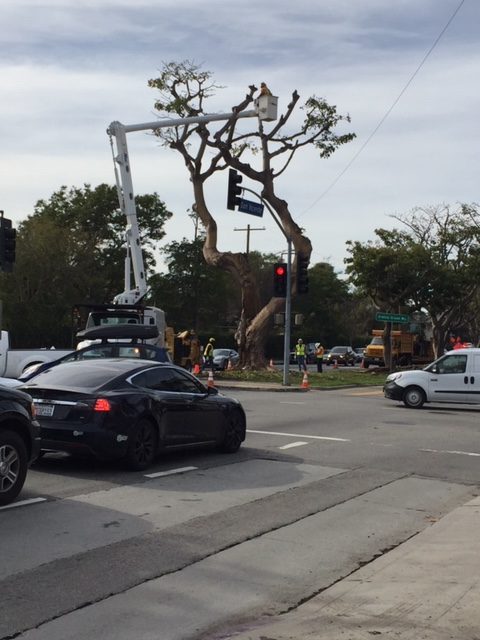
It was the community that rallied together to foster the beloved trees. Freedman continues, “The community took on the responsibility because the City was trimming trees once every seven years at some point in its history. The corals need annual trimming as they are fragile and branches break if too heavy.” Freedman adds, “A group of dedicated residents led by Barbara Goldenberg kept watch for decades. Even though some have grown quite large, they are very much affected by factors beyond human control.”
According to Donald R. Hodel, Environmental Horticulture Advisor for the University of California, Cooperative Extension for 36 years, a combination of issues have contributed to the loss of California’s coral trees. “There are two main problems, and both of them are new pests that have come into Southern California in the last several years,” Hodel begins. “One is called the Erythrina Stem Borer. That’s a moth which lays eggs in the tips of the branches in the leaves. The eggs hatch and the larvae burrow into the tip of the branch and kill it. The plants response is to put out new growth, but the moths lay eggs in those. Eventually all the tips are dead and growth stops.” Hodel continues, “There’s another small insect called the Invasive Shot Hole Borer. This one lands on the trunk or main branches and burrows into the trunk where it lays its eggs. This one is doubly bad because it brings with it a pathogenic fungus. Not only does the insect make mechanical damage to the trunk and branches through all these holes, but the fungus starts growing and attacks the tree. When it lays eggs, the eggs hatch and the larvae needs something to feed on and so they feed on the fungus. They don’t feed on it enough to kill it so then the fungus kills the trees too.”
While coral trees are native to South Africa, the similarities in climate between Los Angeles and South Africa make California an ideal home for coral trees. Hodel explains, “Coral trees come from a climate quite like ours, and they don’t really like a lot of water. But people usually plant them in places where they get watered way too much and they fertilize and they get all this rank growth. The branches often fall out. Once established, these trees probably don’t need much water other than rain.” The coral trees lining San Vicente are the most prone to overwatering and fertilization.
Despite their beauty and important place in California’s landscape, the prognosis for the coral trees is bleak. A sick tree at the corner of Bundy and San Vicente was removed just last week. Hoder explains, “There has been some success with spraying to control the Invasive Shot Hold Borer. There’s a little bit of success controlling the Erythrina Stem Borer, but really this means constantly spraying the trees. I don’t know if people would be willing to tolerate that.” Hoder continues, “The way it’s looking right now, it’d be really difficult to have coral trees. It’s quite sad.”