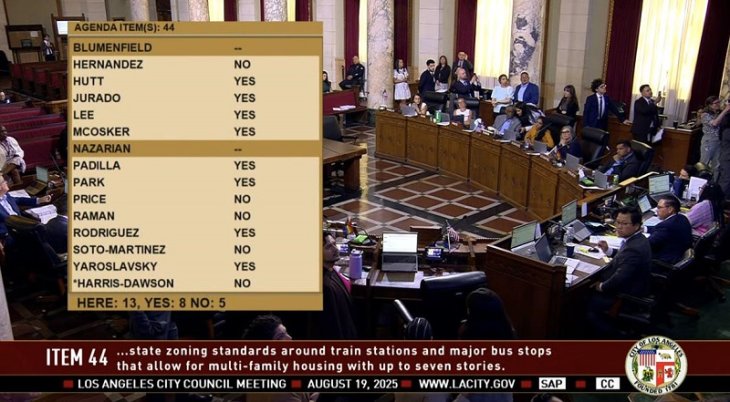
P-54 gives birth to first litter
By Kerry Slater
Acknowledging the civic unrest across the nation, Santa Monica Mountains rangers made an announcement that they hope can bring a small smile to faces: the recent discovery of a den of mountain lion kittens
“We want to acknowledge that times are tough. Not only are we still dealing with a deadly pandemic, but our nation is engaging in an intense and emotional dialogue about issues related to race and civil rights,” said Ranger Ana Beatriz Cholo with the Santa Monica Mountains National Recreation Area. “With this in mind, we hope that our recent discovery of a den of mountain lion kittens can perhaps bring a small smile to your face today.”
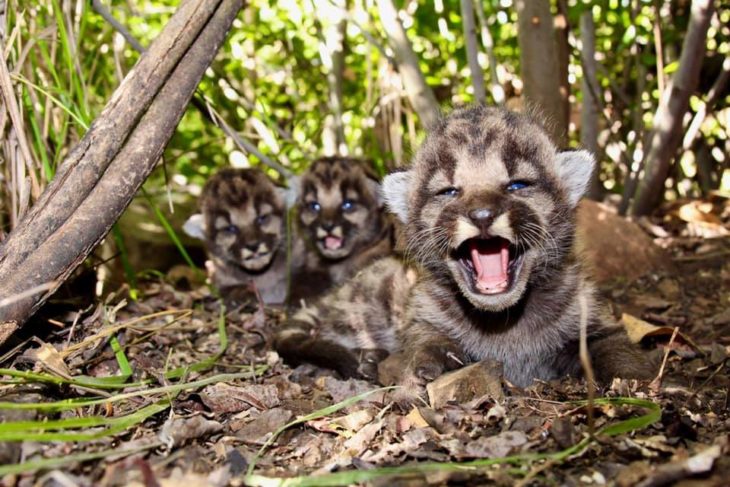
P-54, a three-year old mountain lion living in the Santa Monica Mountains, recently gave birth to a litter of kittens – males P-82 and P-83, and female P-84, according to National Park Service biologists. Researchers believe this is her first litter.
It’s always good news to discover a new litter of kittens, but biologists are hopeful for another reason: the presumed father, male mountain lion P-63, may have just brought something that is much needed into the Santa Monica Mountains – genetic diversity.
More than four months ago, P-63, the only adult male radio-collared mountain lion living in the Santa Monica Mountains, was repeatedly “located” with P-54 over two days, which is generally an indication of a mating interaction. Approximately 90 days later, researchers noticed a series of localized GPS locations indicating that either P-54 was feeding at a kill site or that she had given birth.
This may also be the first time that P-63 has fathered kittens.
“The last litter of kittens that we marked at a den was from P-19, during the summer of 2018,” said Jeff Sikich, a biologist who has been studying mountain lions for Santa Monica Mountains National Recreation Area since 2002. “That litter was likely the product of inbreeding, which is just one of the serious problems facing the isolated mountain lion population in the Santa Monica Mountains south of the 101 Freeway. We’re hoping this circumstance is totally different, but only genetic testing will tell us for sure.”
After Park Service biologists discovered P-54’s litter, they weighed and examined the trio and determined that all appeared healthy. Each kitten was given an ear tag to help identify them in the future, samples were taken for genetic testing, and all were returned to the den. P-54’s kittens were estimated to be 19 days old at the time of tagging.
P-54 has been tracked by biologists in the Santa Monica Mountains practically her entire life. She was born in January 2017 and the following month, NPS researchers marked her with a tracking device as a kitten while her mother, P-23, was away from the den.
In January 2018, P-54’s mother, P-23, was found dead near the side of Malibu Canyon Road, after being struck by a vehicle. P-54 was one year old at the time of her mother’s death, which is during the early end of when kittens typically leave their mother. Fortunately, she survived.
The new litter’s likely father, P-63, was initially captured at approximately 15 months of age with his mother P-62 in February 2018 and outfitted with a GPS collar. Both cats were captured north of the 101 Freeway in the Simi Hills. Since then P-63 has crossed that freeway a total of three times and has stayed in the Santa Monica Mountains since December of 2018.
Southern California’s extensive freeway network presents a major barrier for wildlife, which is particularly a concern for the mountain lion population largely isolated in the Santa Monica Mountains. Planning and fundraising for a wildlife crossing over the 101 Freeway in the Liberty Canyon area of Agoura Hills is in progress. The bridge would provide a connection between the small population of lions in the Santa Monica Mountains and the large and genetically diverse populations to the north.
This is the 17th litter of mountain lion kittens marked at a den site over the course of our long-term study. Three additional litters of older kittens (all at least six months old) were discovered and marked when they had already left their den site.