Two Lawsuits Accuse Top Carriers of Price-Fixing and Violating Antitrust Laws
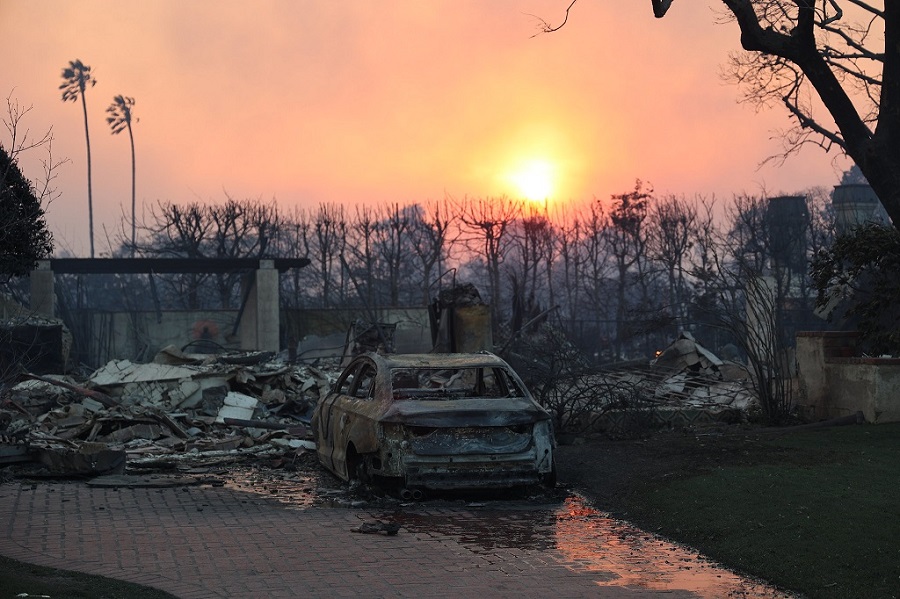
Attorneys representing homeowners impacted by California’s January wildfires have filed a pair of lawsuits in Los Angeles County, accusing major insurance companies of orchestrating a scheme to restrict traditional coverage in high-risk fire zones, forcing policyholders into the state’s limited and expensive FAIR Plan.
The legal complaints, brought by Larson LLP and Shernoff Bidart Echeverria LLP, allege that State Farm, Farmers, and more than 20 other insurers, which collectively hold about 75% of the state’s home insurance market, colluded to cancel or deny policies in areas including Malibu, Pacific Palisades, and Altadena just before the fires hit. The plaintiffs argue that this abrupt and coordinated withdrawal violated California’s antitrust and unfair competition laws, leaving thousands of residents financially exposed during a time of crisis.
Rather than providing the standard, comprehensive coverage homeowners had relied on for years, the insurers allegedly funneled affected residents into the California FAIR (Fair Access to Insurance Requirements) Plan—a last-resort option designed for those who cannot secure private insurance. FAIR Plan policies cap payouts at $3 million and cost, on average, more than twice as much as typical policies, while offering far more limited protections.
“Insurance should be there when disaster strikes,” said attorney Michael J. Bidart of Shernoff Bidart Echeverria LLP. “Instead, these companies pulled the rug out from under our clients, saddling them with overpriced, inadequate coverage when they needed it most.”
One of the complaints, Todd Ferrier et al. v. State Farm Group et al., was filed on behalf of homeowners who lost properties in the January wildfires. The plaintiffs claim they had sufficient insurance coverage until their policies were abruptly canceled or non-renewed, forcing them to purchase FAIR Plan policies just months before the disaster. As a result, their insurance payouts fell far short of covering their losses.
The second case, Anthony Canzoneri v. State Farm Group et al., seeks class-action status on behalf of all policyholders who were pushed into the FAIR Plan after January 2023, when the alleged conspiracy is alleged to have begun. It asserts that homeowners throughout California have paid steep premiums for substandard policies as a result of insurers’ coordinated effort to limit exposure in wildfire zones.
The suits also highlight what they describe as structural flaws in the FAIR Plan system. Insurers are the sole voting members of the plan’s governing body and are required to fund the program in proportion to their market share. The plan was underfunded at the time of the fires, according to the lawsuits, and changes approved by the state in 2024 now allow companies to recoup those contributions by raising premiums for customers in low-risk areas, creating additional incentives for insurers to reduce their risk by pushing more customers onto the FAIR Plan.
Stephen G. Larson, co-counsel in the litigation, said the case is not only about seeking damages for victims of the wildfires but also about restoring competition and fairness to California’s insurance market. “This kind of coordinated market manipulation is exactly what antitrust laws are meant to prevent,” Larson said. “We intend to hold these companies accountable and ensure Californians have access to the coverage they need and deserve.”
While the lawsuits focus on those directly impacted by the wildfires, others have shared similar experiences. Alicia Kalvin, a homeowner in a fire-prone area, said she was dropped by her insurer last July and denied coverage by multiple other providers. “I was told the FAIR Plan was my only option,” she said, as quoted by NBC News Palm Springs. Though her house survived the fires, toxic ash rendered it uninhabitable, and she remains uncertain whether her insurer will cover rental assistance or restoration costs.