By Tom Elias, Brentwood News Columnist
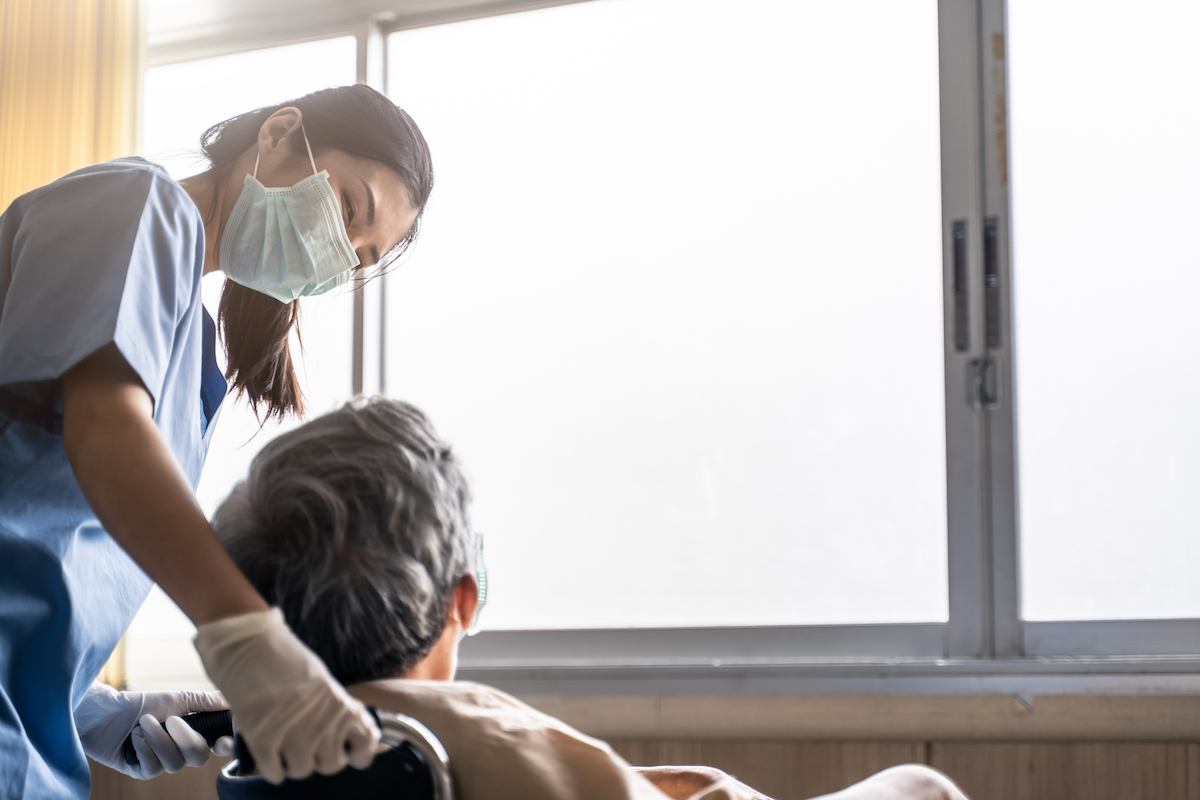
The good news in California nursing homes this summer is that some are allowing their residents to see visitors at long last, but almost exclusively outdoors and in very controlled circumstances where the guests have little chance to see what’s happening inside the homes.
This small, far-from-universal change is largely the result of a slight improvement in a key state guideline governing nursing homes.
The change: The state Department of Public Health (DPH) no longer merely recommends that nursing homes allow residents to designate one person to visit during the COVID-19 pandemic if the visitors distance, don masks and other personal protective equipment. In late June, the DPH began mandating that nursing home denizens “shall” be allowed to pick a guest.
That’s a big improvement for the relatively few residents of the homes who now get occasional visits. Previously, all visitors had been banned from the homes, even state inspectors. This amounted to carte blanche for many nursing home managements to reduce staff (especially with state staffing requirements suspended early on) and keep disabled residents in bed for days at a time. Even on days when they’re allowed out of bed, staffers often stash them back there around mid-afternoon because workloads are so large they would not otherwise have time to serve dinner to all their patients.
Essentially, visitors have lost their previous role as the main watchdogs over nursing home practices.
The intent of the original visitor ban was to keep the coronavirus plague out of the homes. That policy has failed, what with about 49 percent – almost half – of all California COVID-19 deaths occurring among those residing in nursing homes, as of early July.
“(The ban) has been an extreme hardship for most nursing home patients,” said Lori Smetanka, executive director of the National Consumer Voice for Quality Long Term Care. “It has led to significant physical, social and psychological harm for many thousands of residents. Their needs are worsening without families to visit them.” She added that even when virtual visits via services like Zoom and Facetime are arranged, “they often prove disruptive to residents, especially those with cognitive impairments.”
That adds to a climate described this way by one 76-year-old physically handicapped nursing home resident who retains all his mental faculties: “The nursing home establishment makes people feel like ‘throw-aways,” he wrote in an email. “We feel much like abandoned pets or children with disabilities. This makes it difficult to maintain the attitude and motivation you need to feel like a human being in here.”
Lawyer Tony Chicotel of the California Advocates for Nursing Home Reform organization describes the last four months for a typical resident of this state’s nursing homes as “very much like solitary confinement,” adding that most are even worse off than that, because they share rooms and get little privacy outside their own thoughts.
“This is institutionalized isolation,” Chicotel said. “Some call it a form of solitary confinement. It’s become inhumane and cruel. This has been done to people without any consultation or due process. And the no visitor policy has been a colossal failure, too.” In fact, most of the COVID-19 that has so severely hit nursing homes came into them with staffers, who often must work two jobs because of their low pay. Even if one home where they work is “clean,” they can become infected at their second job or in crowded conditions where they live.
Then there’s assisted living, where residents often pay large sums for rooms and apartments. They also have had no visitors, reports Chicotel. But unlike nursing home residents, they are allowed out for excursions, medical appointments or other needs. The rub, says Chicotel: On their return, most assisted living homes require residents who leave even for short times to quarantine for 14 days, never leaving their rooms during that time for any reason.
As a result, few ever leave and many residents suffer isolation similar to nursing home patients.
If a society can be judged by the way it cares for its grandparents and other elders, what does all this say about California and the rest of America, where the same situations apply almost everywhere?
Email Thomas Elias at tdelias@aol.com. His book, “The Burzynski Breakthrough: The Most Promising Cancer Treatment and the Government’s Campaign to Squelch It,” is now available in a soft cover fourth edition. For more Elias columns, visit www.californiafocus.net